For anyone in the field of AI and ML, they probably do know all of these terms. But how do you explain these to someone new. Let’s try understanding this.
USE CASE:
- Mark wants to plan a trip to Georgia in Europe and he wants to use an LLM for this.
INTERACTION WITH LLM:
Attempt 1:

Mark wanted information on Georgia in Europe but the LLM has returned information about the state Georgia in the US. Mark realised the mistake and corrects his prompt.
Attempt 2:
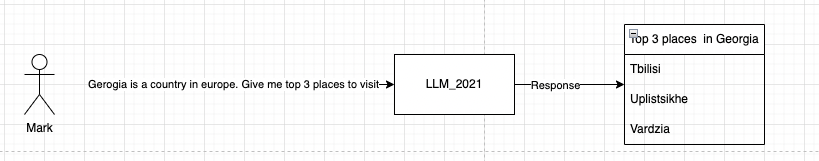
PROBLEM:
- The LLM behaved as expected in attempt 2 but not in attempt 1.
- This is because we gave the LLM context(regarding the location of Georgia) as we asked it the question.
- In very simply term, the issue of LLM giving response not expected is called hallucination.
LEARNING:
- To give relevant responses LLM needs context about the questions that it would be asked.
SOLUTION:
Let’s look at one of the solutions. We add an external data source and feed it with information on the domain area that the LLM has to work with. We use this to construct context aware prompts
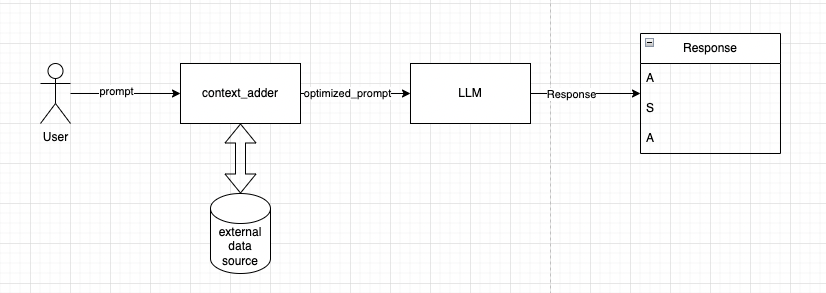
FLOW:
- User sends prompt to system
- We keep all the new information that we collect in an external data source.
- We take the user prompt, get context about the question from the external data source.
- We send the optimised context aware prompt to LLM.
- We get results from LLM
VECTOR DB AND RAG:
- The architectural approach that we have taken to make use of custom Data to get better responses from existing LLM is RAG or Retrieval augmented generation
- The external data source here is VECTOR DB.
SYSTEM DIAGRAM:
Now that we have seen a representation lets look at how an actual system diagram would look like:-
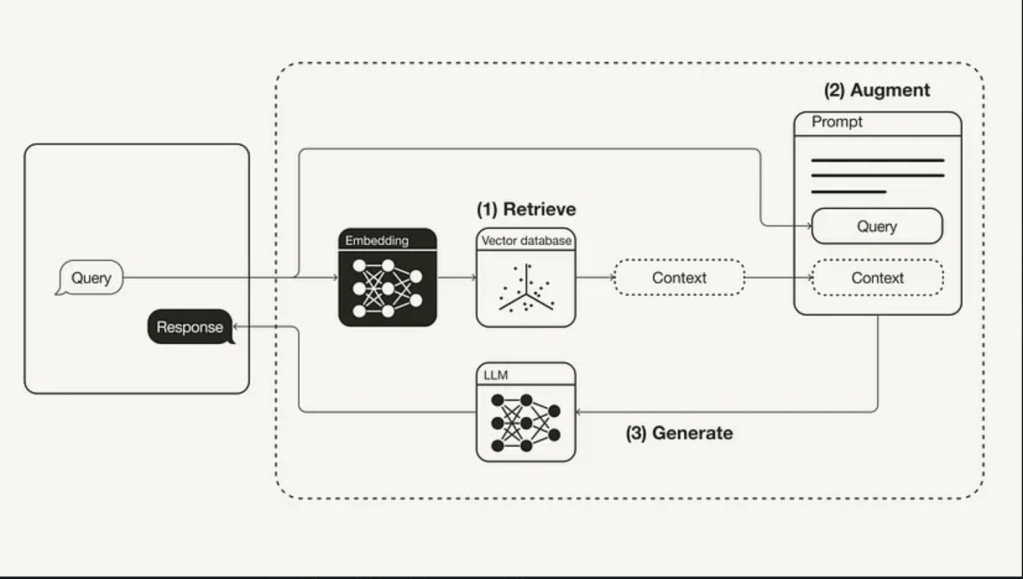
Flow:
- User sends prompt to system
- We keep all the new information that we collect in an external data source.(vector database and embeddings)
- We take the user prompt, get context about the question from the external data source.(context aware prompts)
- We send the optimised context aware prompt to LLM.
- We get results from LLM
ADVANTAGES OF RAG:
- Reduce hallucinations in LLM results
- LLM can also cite sources during giving responses
- Very helpful with knowledge intensive tasks
- No extra compute required which would have been required to fine tune the existing model.
NOTE:
This article aims to introduce RAG, but which technique works better would depend on use case to use case. And the field of LLM’s is evolving ever so fast, so it is important to understand and upskill.
WHAT NEXT:
Now that you know rag you might be wondering what next, where to read more from. One very good place is the checking out the short courses from deeplearning.ai
2 thoughts on “Understanding RAG and Vector DB”